The UAE is known for its rapid economic development and ambitious infrastructure projects, but it’s also gained attention for its high per capita carbon emissions. As the world faces mounting pressure to mitigate climate change, understanding the sources of these emissions and exploring ways to reduce them is crucial for creating a sustainable future.
UAE’s Per Capita Emissions in Context
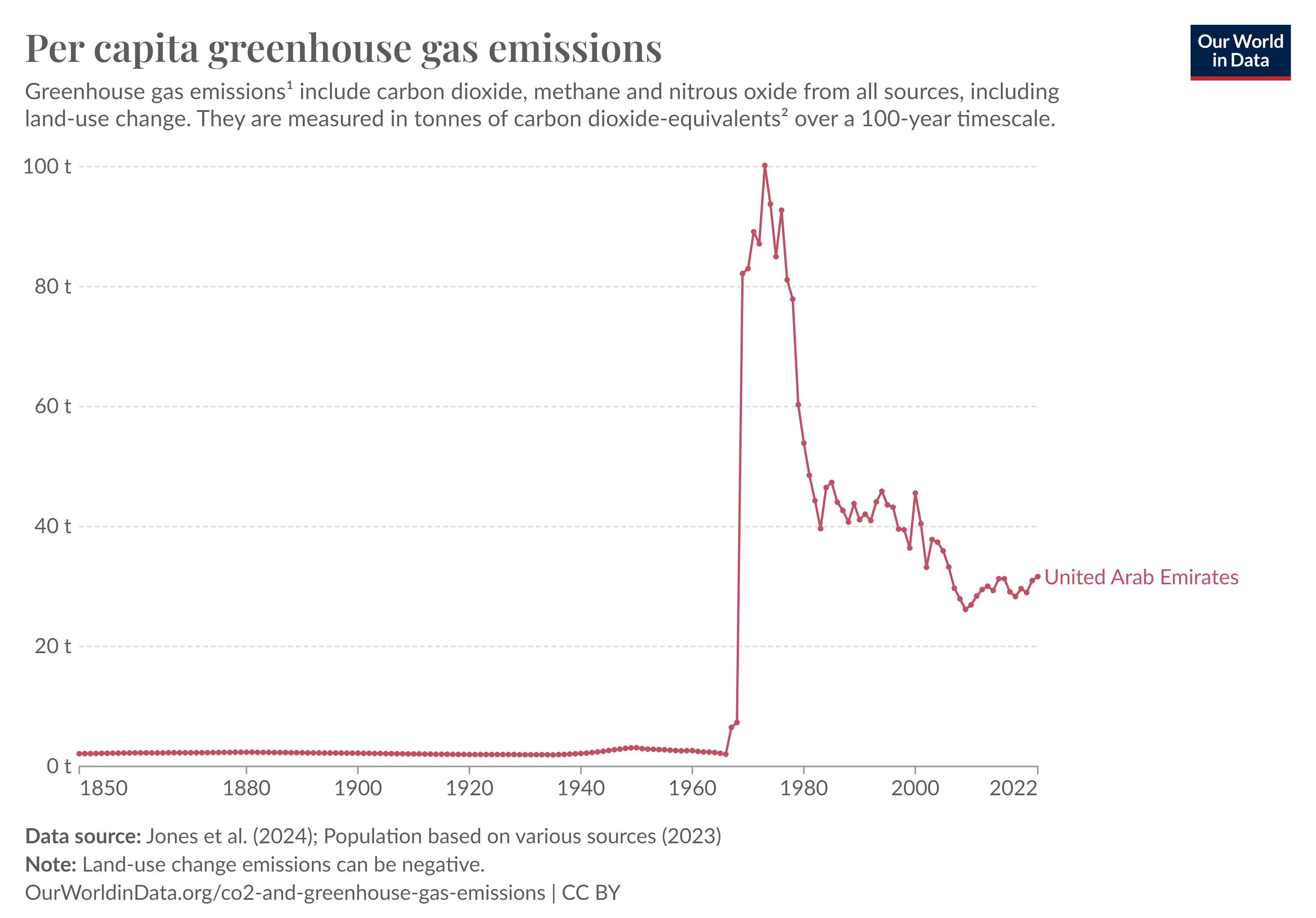
The chart illustrates per capita greenhouse gas emissions, expressed in ‘carbon dioxide equivalents’ (CO2e). This metric accounts for the varying impacts of different greenhouse gases on global warming. Since one tonne of a specific gas may not cause the same amount of warming as another, the emissions of each gas are multiplied by its Global Warming Potential (GWP). GWP measures how much warming a tonne of a particular gas generates compared to a tonne of carbon dioxide (CO2), making it possible to present all emissions on a comparable scale.
As of the latest data, the UAE’s per capita greenhouse gas emissions sit around 32 metric tons per person per year, far above the global average of approximately 4.5 metric tons. Here’s a deeper dive into the key factors driving this figure:
- Energy-Intensive Economy The UAE’s economy has been historically powered by oil and gas, and while the country is making a conscious shift toward diversification, fossil fuels still play a major role. Energy production, industrial activities, and desalination plants are significant contributors to the country’s overall emissions.
- Desert Climate and Energy Demand The UAE’s climate, with average summer temperatures soaring above 40°C (104°F), necessitates widespread use of air conditioning, which consumes vast amounts of electricity. The energy required to maintain comfortable living and working environments is a major contributor to high per capita emissions.
- Rapid Urbanization and Infrastructure Growth Since its formation, the UAE has undergone rapid urbanization. Iconic skylines filled with skyscrapers, malls, and hotels require large amounts of steel, concrete, and glass—all materials that are carbon-intensive to produce. Moreover, the construction and upkeep of this infrastructure involve considerable energy use.
- Transportation and Fuel Consumption The UAE’s car-centric culture, combined with a love for large, fuel-inefficient vehicles, adds another layer to the emissions problem. Despite efforts to expand public transport, the vast majority of residents still rely on private vehicles due to the sprawling nature of cities and the challenges posed by extreme heat during much of the year
- High Consumption Patterns The UAE has one of the highest consumption rates globally, ranging from energy use to water and consumer goods. The demand for imported goods (including food) adds to the country’s carbon footprint, as shipping and transport activities contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
Breaking Down Emissions by Sector
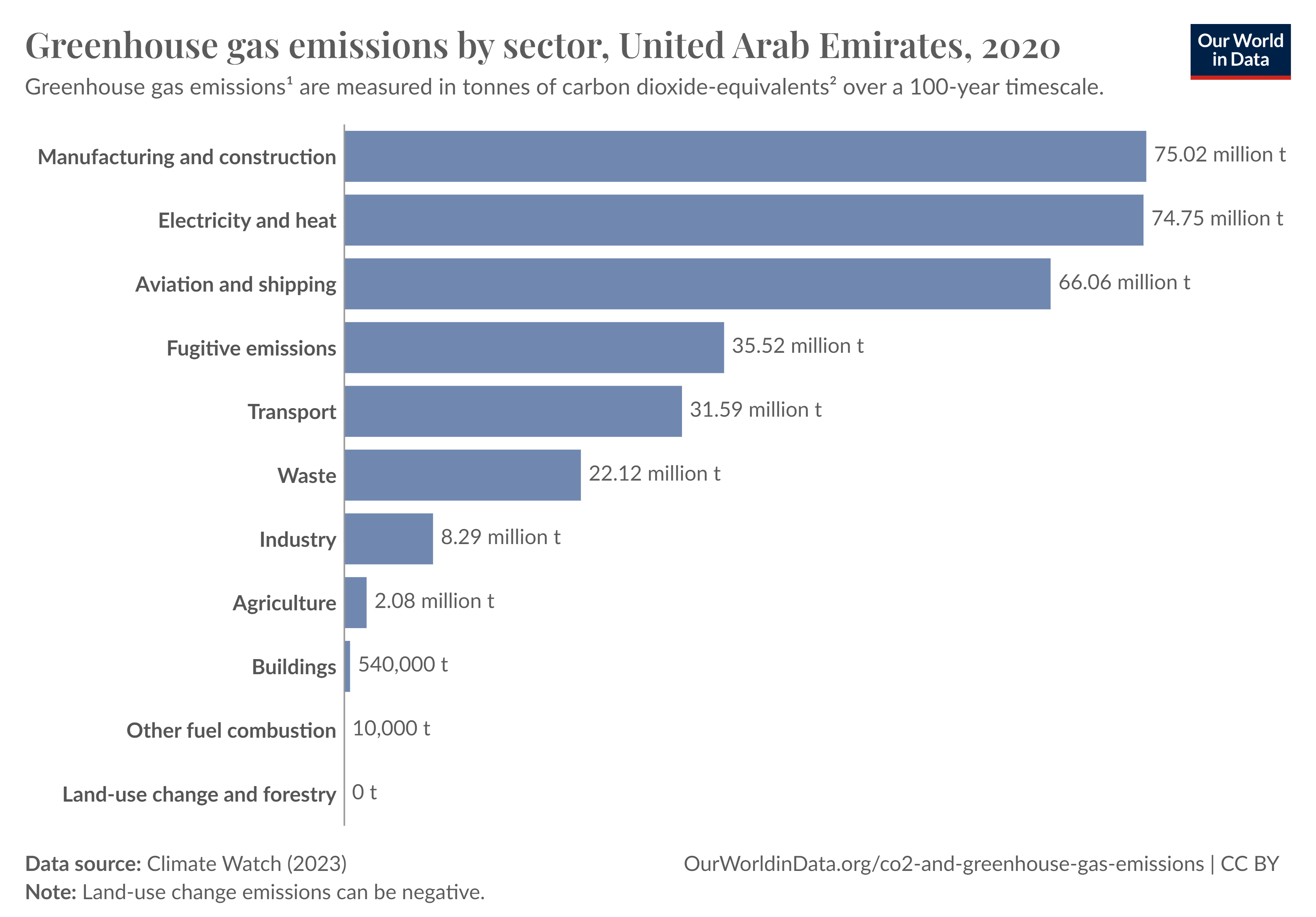
Greenhouse gas emissions in the UAE primarily stem from several key sectors:
- Manufacturing and Construction and Electricity and Heat generation are the largest contributors, accounting for nearly 150 million tonnes combined.
- Aviation and Shipping play a significant role, adding 66 million tonnes.
- Fugitive Emissions from industrial processes contribute 35.52 million tonnes.
- Transport and Waste sectors each account for around 30 million tonnes of emissions.
Government Efforts and UAE’s Vision for Sustainability
The UAE has not ignored these challenges and has, in fact, been quite proactive in its sustainability goals. Several national initiatives are in place to lower the country’s overall emissions:
UAE Net Zero 2050 Strategic Initiative
In line with global efforts to combat climate change, the UAE has pledged to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050. This ambitious goal aims to balance the country’s carbon output with its efforts to remove or offset emissions. The UAE is the first country in the Middle East to commit to this target.
Massive Investment in Renewable Energy
The country has invested heavily in renewable energy projects, including solar, wind, and nuclear energy. The Mohammed bin Rashid Al Maktoum Solar Park, for instance, is one of the largest solar projects in the world, and the Barakah Nuclear Plant is set to provide a significant portion of the country’s electricity while generating zero carbon emissions. When fully operational, the Barakah Nuclear Energy Plant is expected to prevent up to 22 million tons of carbon emissions every year, equivalent to removing 4.8 million cars from the roads.
Promotion of Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Public policy plays a critical role in the UAE’s transition to e-mobility. The government has already taken significant steps by converting 20% of its federal government agency vehicles to electric powertrains. Initially, the UAE set an ambitious target to have 30% of public sector vehicles and 10% of all vehicles on the road be electric (EV or hybrid) by 2030. This transition is supported by incentives such as free vehicle registration, free parking, reduced charging fees, and discounted tolls for EVs.
In a bold update during COP28 in 2023, the UAE Minister of Energy and Infrastructure announced that the country aims for electric and hybrid vehicles to account for 50% of all vehicles on its roads by 2050. This is in tandem with plans to triple power generation from renewable sources, further advancing the country’s sustainable mobility efforts.
Dubai is already leading the charge with a rapidly growing number of EVs on its roads. According to the Dubai Electricity and Water Authority (DEWA), the city recorded 25,929 electric vehicles by the end of December 2023, marking a significant rise from the 15,100 EVs reported just a year earlier.
Water and Waste Management
The UAE has launched initiatives to manage its water resources more efficiently and reduce waste. For example, projects like the Tarsheed initiative in Abu Dhabi focuses on reducing water and electricity consumption per capita by 20% by 2030.
Driving Change at the Individual Level: What Can You Do?
While government initiatives set the stage for large-scale change, individuals have the power to make an impact as well. Here’s how you can help drive the UAE toward a lower-emission future:
- Opt for Renewable Energy in Your Home
Opt for energy-efficient solutions like LED lighting and smart appliances. Residents can also inquire if their building participates in green energy programs or offsetting initiatives, making it easier to lower your carbon footprint. Residents of villas can consider installing solar panels to harness the abundant sunlight and reduce their reliance on fossil fuels. - Cut Energy Use in Your Household
With air conditioning being a major contributor to household energy consumption in the UAE’s hot climate, upgrading to energy-efficient appliances, using smart thermostats, and insulating your home can make a substantial difference. Simple actions, such as turning off the air conditioning when you travel, unplugging devices when not in use, and reducing water heater usage, can collectively lead to significant energy savings. - Switch to Sustainable Transportation
Using public transport, walking, biking, or adopting an electric vehicle are all impactful ways to reduce transportation emissions in your daily life. When it comes to longer trips, especially air travel, being mindful of your flight choices can also significantly lower your carbon footprint.
Flying Responsibly: Understanding Your Impact
Air travel is one of the most carbon-intensive forms of transportation. A single flight can emit more CO2 than driving a car for a year. To minimize your impact, consider these points:
- Business Class vs. Economy Class: The carbon footprint of a business class seat is significantly higher than that of an economy seat due to the extra space allocated per passenger. Opting for economy class whenever possible can reduce your environmental impact.
- Short Haul vs. Long Haul Flights: While long-haul flights tend to have lower per-kilometer emissions, they still contribute heavily to overall emissions due to the long distances covered. Choosing direct flights, which are more fuel-efficient than those with layovers, can also make a difference.
For local and regional travel, consider alternatives like high-speed trains or buses, which offer a much lower emissions profile than flying. Learn more.
- Change Your Diet
The food you eat also impacts your carbon footprint. Eating more plant-based meals and reducing your consumption of meat, particularly beef, can significantly lower your emissions. - Reduce, Reuse, Recycle
Simple lifestyle changes like reducing waste, avoiding single-use plastics, and supporting circular economy initiatives help reduce emissions. Reusing items and recycling materials like plastic, glass, and metal reduces the need for new resource extraction and production. - Offset Your Carbon Footprint
For emissions you can’t avoid, carbon offset programs are an excellent solution. Many programs allow you to contribute financially to environmental projects that absorb CO2, such as reforestation or renewable energy development. - Support Local
In the UAE, there are many local businesses that prioritize sustainability by offering eco-friendly products and services. Supporting these homegrown brands not only reduces the carbon footprint associated with imports but also encourages a more sustainable local economy. By choosing local, you contribute to the growth of businesses that are committed to creating positive environmental impacts.
Explore some of the incredible brands featured in our Brand Spotlight series to discover more about their sustainable practices and how you can support them.
- Support Initiatives
Participating in community initiatives like beach cleanups and tree planting can make a significant difference in the fight against environmental degradation. These activities not only help restore and protect natural habitats but also foster a sense of community and shared responsibility for our planet.
- Beach Cleanups: By joining a local beach cleanup, you can help remove litter, reduce pollution, and protect marine life. Many organizations in the UAE coordinate these events, providing an opportunity to meet like-minded individuals who are passionate about environmental conservation.
- Tree Planting: Trees play a crucial role in improving air quality, enhancing biodiversity, and combating climate change. By participating in tree planting initiatives, you can contribute to reforestation efforts and the overall health of the ecosystem. Look for local programs that aim to plant native species, which are better suited to the UAE’s climate and help support local wildlife.
These are just a few examples of initiatives you can get involved in. Participating in such activities not only helps protect and preserve the environment but also fosters a sense of fulfillment and community spirit. By joining forces with friends and family, you can make a tangible difference in the UAE’s natural beauty while creating lasting memories together.
Learn more about How Your Daily Habits Shape Our Planet’s Future
A Call to Collective Action
It’s clear that the UAE faces unique challenges in reducing per capita emissions due to its economic reliance on energy, urban development, and climate conditions. However, the country is also poised to be a leader in the Middle East in sustainability efforts. With significant investments in renewable energy, innovative government policies, and a shift toward more sustainable practices, the future looks promising.
That said, the responsibility to drive change falls on all of us—individuals, businesses, and governments alike. Small, conscious decisions we make in our everyday lives can significantly reduce our carbon footprints and contribute to the UAE’s vision of a sustainable, low-emission future. By working together, we can turn the tide on climate change and help secure a cleaner, healthier environment for generations to come.
